Today as a part of the Azure Governance and management announcements at Microsoft Ignite 2018 Azure Blueprints Public Preview was announced. Azure Blueprints are a core part of the cloud governance and management story. They go hand and hand with Management Groups and will take the enterprise management story of Azure up a level. In this blog post I will take a deep dive into Azure Blueprints explaining what they are and give an example of how they can be used.
NOTE: This is a long blog post so I have also published this content as a whitepaper. The whitepaper PDF can be downloaded here.
BLUEPRINTS OVERVIEW
At a high-level Azure Blueprints help you meet organizational cloud standards, patterns, and requirements through governed subscriptions enabled and enforced by the grouping of artifacts like ARM templates, Azure policies, RBAC role assignments, and resource groups within a Blueprint.
Blueprints can be used to lay a cloud foundation, as cloud patterns, and group cloud governance frameworks. Blueprints are a one-click solution for deploying a cloud foundation, pattern, or governance framework to an Azure subscription. Think of an Azure Blueprint as re-usable design parameters for cloud that can be shared and used across an enterprise.
Azure architects typically map out and plan the many aspects of a cloud foundation for an organization such as access management, networking, storage, policy, security/compliance, naming conventions, tagging, monitoring, backup, locations, and more. Now Azure architects can step this designing a step further build these designs as Azure Blueprints and then apply them to subscriptions. The Blueprints give architects a way to orchestrate the deployment of grouped components to speed up the development and provisioning of new Azure environments ensuring they are meeting organizational compliance.
BLUEPRINTS ARE NOT AZURE POLICY
Azure policy is a service targeted to resource properties that exists or when being deployed with allow or explicit deny policies. It is used to ensure resources in an Azure subscription adhere to requirements and standards of an organization.
Azure policies can exist on their own or be a part of an Azure Blueprint. Blueprints do not replace Policy they are one of the Artifact types that make up a Blueprint.
THE MAKEUP OF A BLUEPRINT
Definition
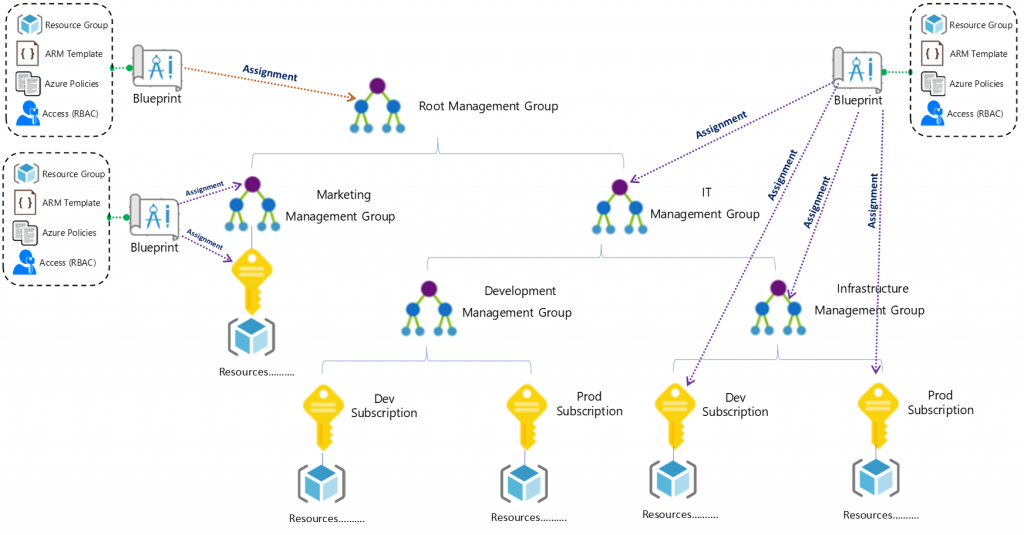
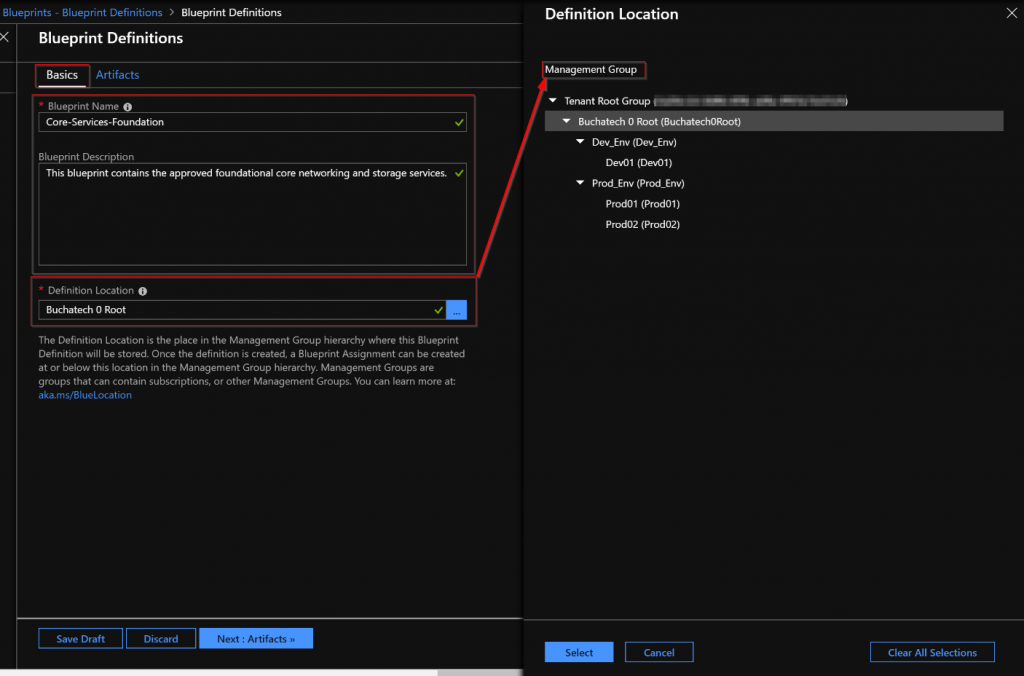
A Blueprint consists of a Definition. The Definition is the design of what should be deployed it consists of the name of the Blueprint, the description and the Definition location. The Definition Location is the place in the Management Group hierarchy where this Blueprint Definition will be stored and determines the level assignment is allowed at. Currently you must have Contributor access to a Management Group to be able to save a Blueprint Definition to it. A Blueprint can be assigned at or below the Management Group it has set in its Definition Location. Here is a diagram to visualize Blueprint Assignment in relation to Management Group hierarchy:
Artifacts
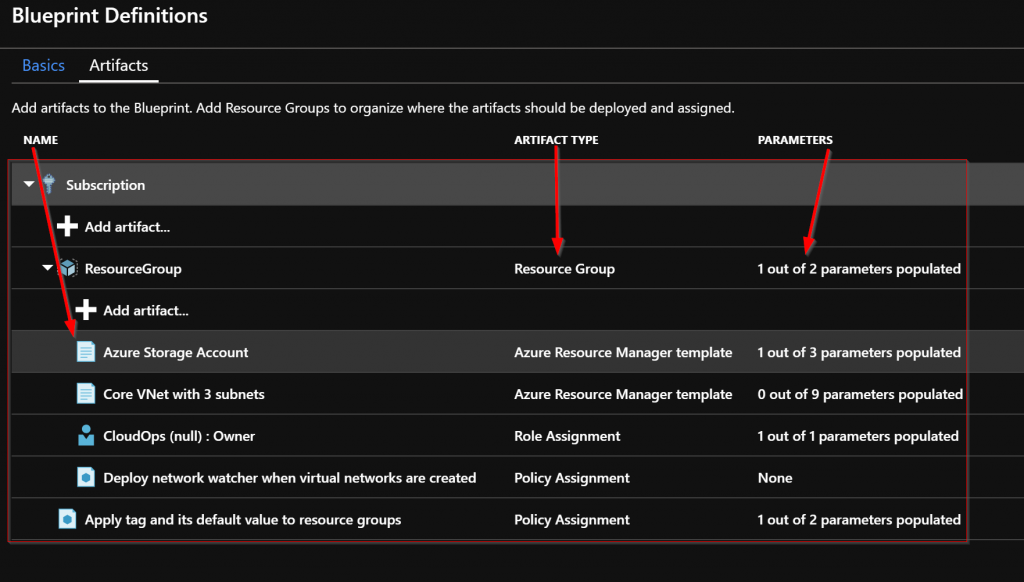
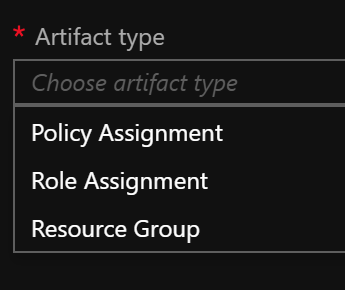
The Definition is where Blueprint Artifacts are added. As of right now the following is a list of the Artifact types:
- Policy Assignments – Lets you add an Azure Policy. This can be a built-in or custom policy.
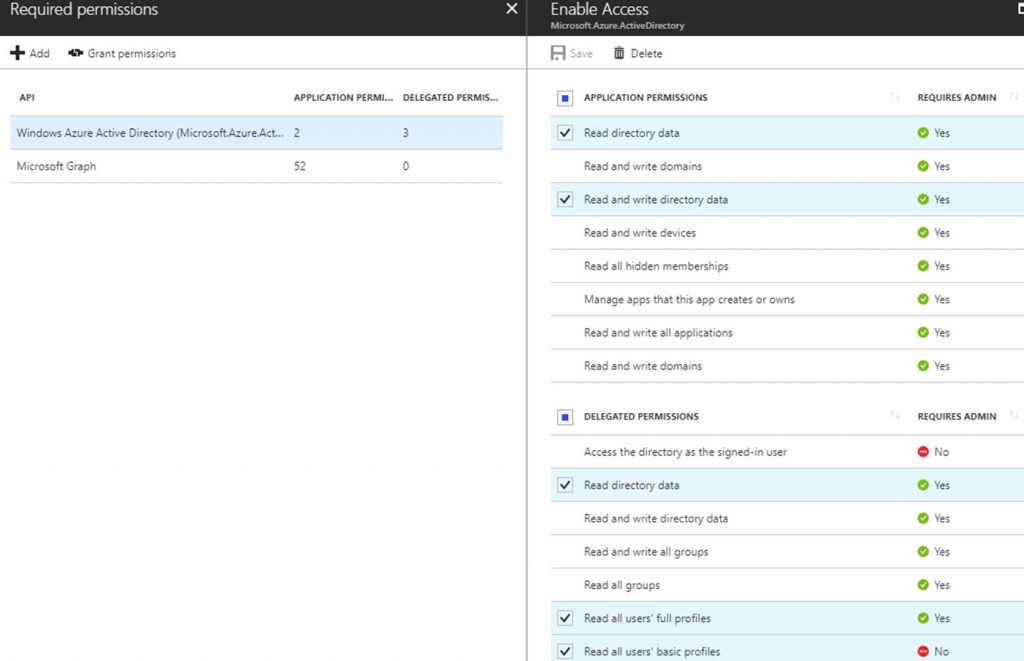
- Role Assignments – Lets you add a user, app, or group and set the role. Only built-in roles are currently supported.
- Azure Resource Manager templates – Lets you add an ARM Template. This does not let you import a parameters file. It does let you pre-set the parameters or set the parameters during assignment of the Blueprint.
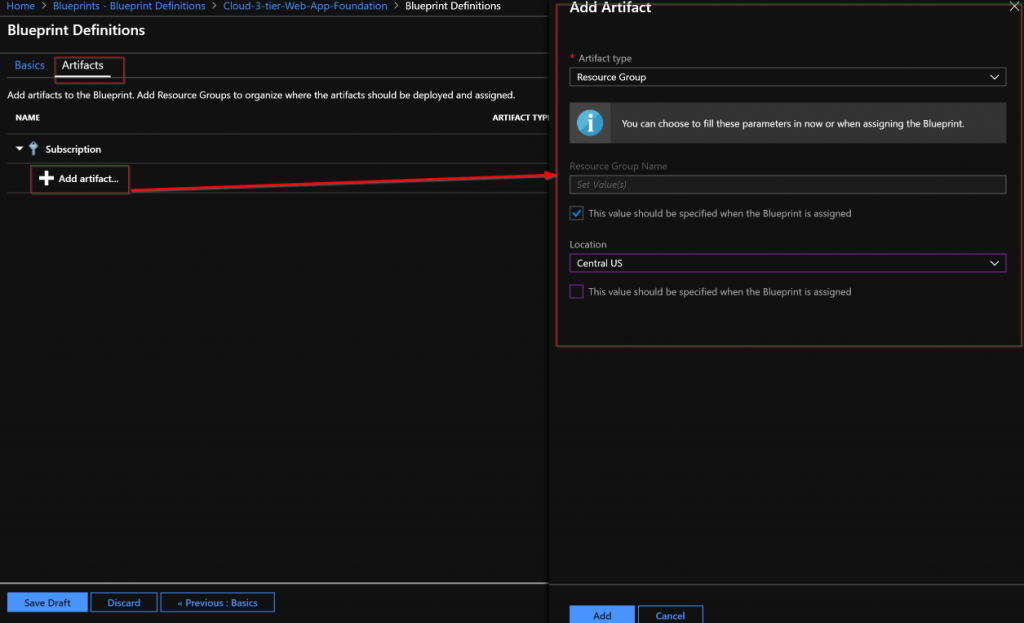
- Resource Groups – Lets you add a Resource Group to be created as a part of this Blueprint.
In my opinion the ARM Template artifact is the most impactful of the Blueprint artifact types because you can define such a variety of resources here. It opens the Blueprint to the power of ARM in general. Hopefully in the future we will see more scripting capability or the ability to load PowerShell scripts, runbooks, and or Functions.
There are two levels in the Artifacts. The first level is Subscription. The second level is Resource Group. Resource Group artifacts cannot be added to a Resource Group artifact. A Resource Group artifact can be created in a Subscription. An ARM Template artifact can only be created in a Resource Group artifact. A Policy Assignments or Role Assignments can be created at either the Subscription or Resource Group level.
Assignment
After a Blueprint has been built it needs to be applied. Applying a Blueprint is known as Blueprint assignment. The assignment is essentially the “what was deployed” for a Blueprint. This is how the artifacts are pushed out to Azure and used to track and audit deployments in Azure.
Sequencing
When the assignment of a Blueprint is processed the default order of resource creation is:
- Role assignment artifacts at the Subscription level
- Policy assignment artifacts at the Subscription level
- Azure Resource Manager template artifacts at the Subscription level
- Resource group artifacts and its child artifacts (role assignment, policy assignment, ARM Templates) at the Resource Group level
When a blueprint includes multiple Azure Resource Manager templates there may be a need to customize the sequencing order in which the Blueprint will deploy artifacts during assignment. You customize the artifact deployment sequence by deploying a Blueprint from an ARM Template declaring a dependency within it or declaring a dependency within an ARM Template artifact in the Blueprint. You declare a dependency using the dependsOn property in JSON. This essentially is a string array of artifact names.
Resource Locking
In cloud environments consistency is key. Naturally Azure Blueprints can also leverage resource locking in Azure. Blueprints have a Locking Mode. This Locking Mode can be applied to None or All Resources and is determined during the assignment of the Blueprint. The decision on cannot be changed later. If a locking state needs to be removed, then you must first remove the Blueprint assignment.
Some Blueprint artifacts create resources during assignment. These resources can have the following state:
- Not Locked – Can be changed. Can be deleted.
- Read Only – Can’t be changed and can’t be deleted.
- Cannot Edit / Delete – Create, update, and delete within the resource group.
Artifacts that become Resource groups get the state of Cannot Edit / Delete automatically but you can create, update, and delete resources within them.
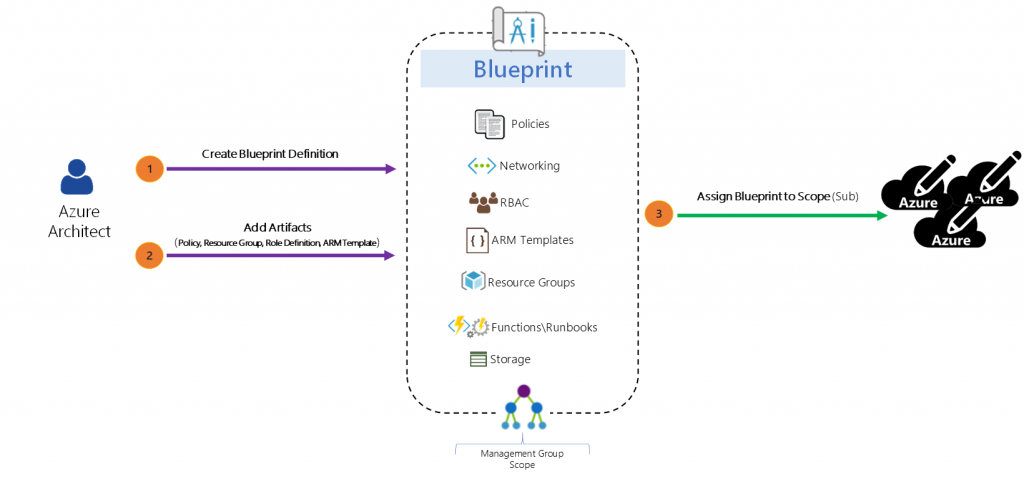
The high-level stages of an Azure Blueprint are Create it, assign it to a scope, and track it.
Anatomy of a Blueprint:
Blueprint does have a REST API. I am not covering the REST API in this blog post as I have not had the opportunity to spend much time working with it yet.
Now let’s look at building and assigning an Azure Blueprint.
BUILD A BLUEPRINT
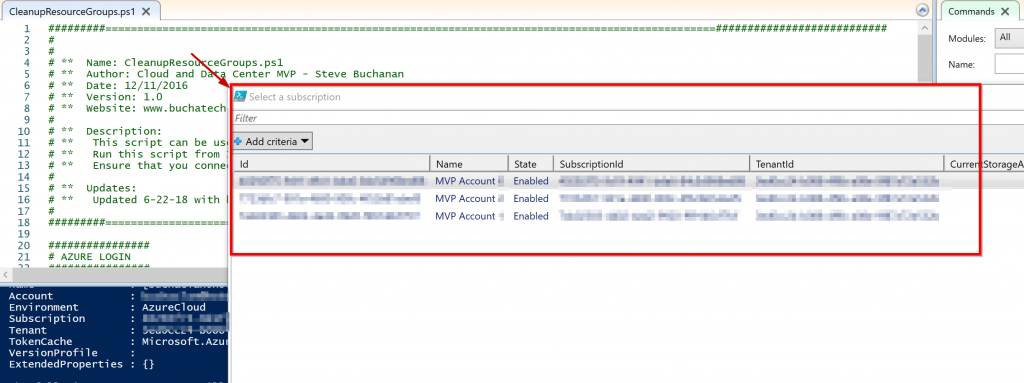
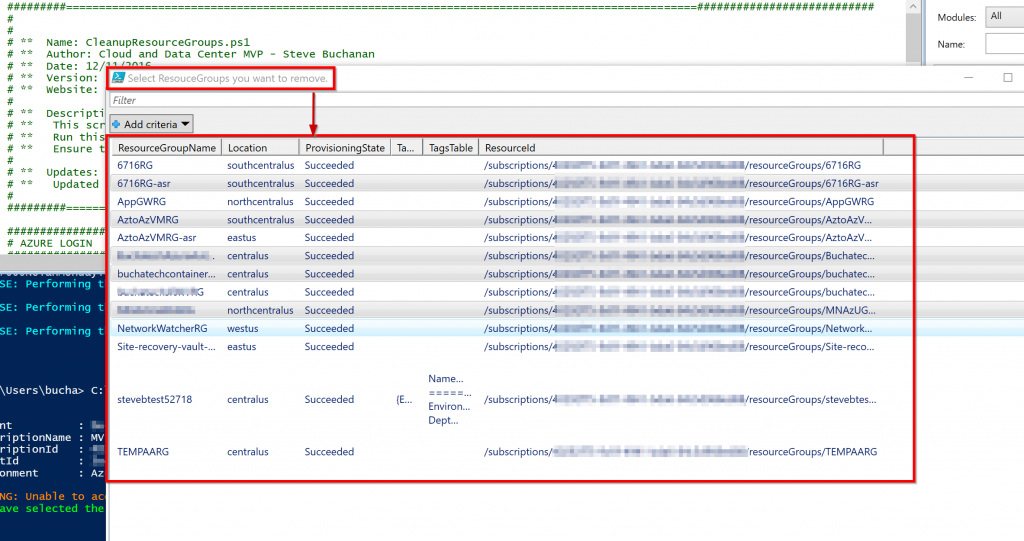
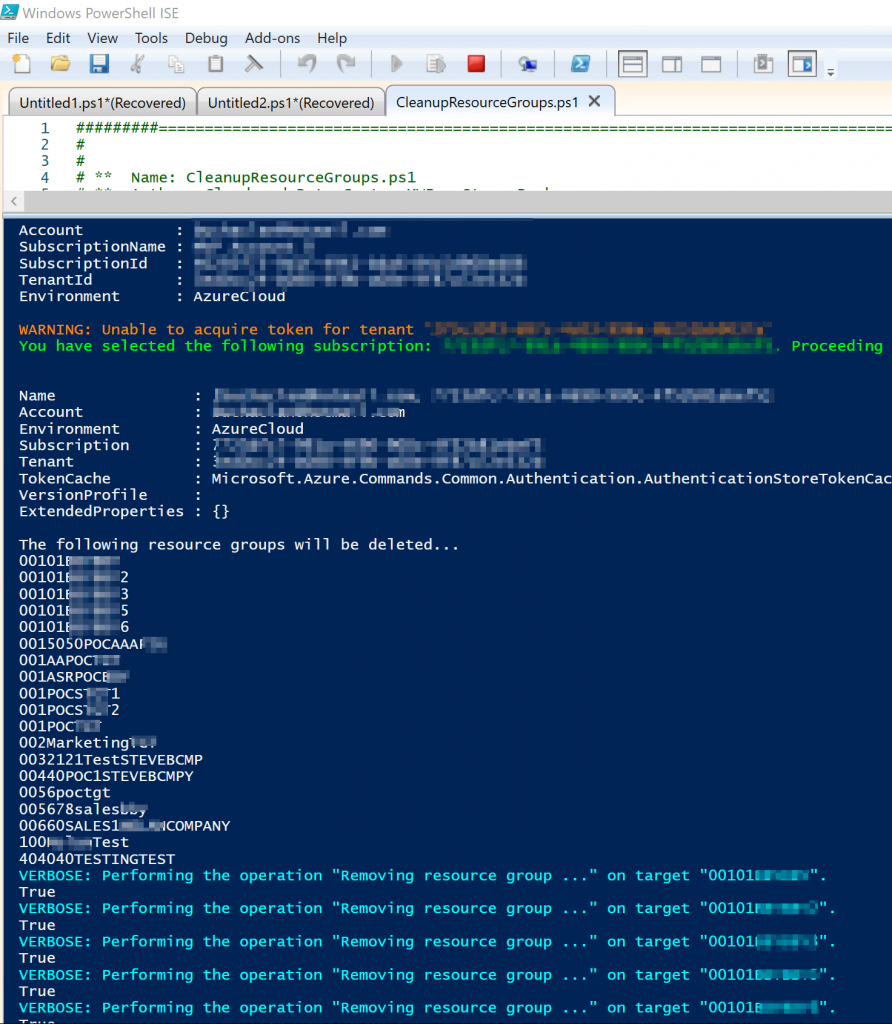
Now I am going to give an example of building and using an Azure Blueprint in a cloud foundation mock scenario. In my mock scenario I have 3 Azure subscriptions. Each subscription should have a Core services Resource Group consisting of a core VNet with 3 subnets, an NSG for each subnet, and the web subnet should be ready for DMZ traffic. For the core VNet and any additional VNet added to the Core Services Resource Group I need network watcher deployed to it.
Each subscription also should have a core storage account and a blob storage that is ready for general storage needs. I want a tag applied to any Blueprint assignment labeling it with the assignment name, so it is easy to track. The last requirement I have is that I need the CloudOps team to automatically be owner of all core services resources. To accomplish all of this I created the following Blueprint:
Now let’s walk through the parts of creating and assigning the Blueprint. The first step is to create the Blueprint Definition.
In the basics step I give it a meaningful name and meaningful description. I set the Definition Location to the root of my Management groups. Doing this will allow me to assign this Blueprint to all 3 subscriptions in turn creating the core services RG in each subscription.
Next the Artifacts need to be added. Note that when adding an Artifact at the Subscription level you have these options as types:
The Resource Group Artifact type is only available at the subscription level and the ARM template Artifact type is only available at the Resource Group level. I added the Resource Group that the core networking and core storage will be deployed into.